The calorie and macro math
Here, we outline the numbers used to determine the calories and macros delivered by the calculator.
Calorie math
This calculator uses the same baseline algorithm as the Precision Nutrition Weight Loss Calculator to calculate maintenance, weight loss, and weight gain calorie needs. It factors in the dynamic and adaptive nature of your metabolism to predict how long it’ll take you to reach your bodyweight goal.
This algorithm is a mathematically validated model based on the NIH Body Weight Planner and adapted from research collected at the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease.
Q:
How do goals change the equation?
A:
For people looking to improve health, the calorie, portion, and macro calculator uses the weight maintenance calories determined by the validated mathematical model inherent to the NIH algorithm.
For people looking to lose body fat, the calorie, portion, and macro calculator uses the validated mathematical model inherent to the NIH algorithm. This takes into account a whole host of anthropometric data, time desired to reach goal, and the adaptive nature of human metabolism.
For people looking to gain muscle, the calorie, portion, and macro calculator uses the validated mathematical model inherent to the NIH algorithm. This takes into account a whole host of anthropometric data, time desired to reach goal, and the adaptive nature of human metabolism.
For people looking to improve athletic performance, the calorie, portion, and macro calculator adds an additional 10% more calories to the weight maintenance requirements calculated by the NIH algorithm. This supports the increased demands of athletic performance.
For people looking to change their body composition with minimal weight change, the calorie, portion, and macro calculator lowers calorie needs by 10% from the weight maintenance requirements calculated by the NIH algorithm. This’ll help facilitate simultaneous fat loss and muscle growth. It should be noted that this approach is most appropriate for individuals who don’t wish to change their body weight by more than 10 to 15 pounds, yet want to improve their body composition.
Macro math
The macronutrients are calculated by many rules.
- Protein is set on a grams per pound of bodyweight basis, at a range of 0.65-1.35 g/lb, depending upon sex, weight, goal, and activity level. (For very low-fat and very low-carb options, protein is set at 20% of calories, not on a bodyweight basis.)
- Protein needs are also set on a sliding scale since, on average, even within the same goal and activity level, heavier folks would generally have a greater body fat percentage than lighter folks. Therefore, they require a smaller amount of protein on a grams per pound basis (though still higher on an absolute basis).
- Then, dependent upon the Macronutrient Preference chosen, either fat or carbohydrates are set at a particular percent of calories (e.g. “Low-fat” is set at 20% calories from fat, and “Low-carb” is at 20% calories from carbs) to determine the allocation of the remaining non-protein calories.
- Finally, the rest of the calories are filled out by the remaining macronutrient (either fat or carbs). Note, if “Balanced” was chosen, the non-protein calories are split evenly between fats and carbs.
Custom macronutrient percentages
When custom macronutrient percentages are entered, those ratios are used to determine all macronutrient and hand-portion calculations. Overriding the macronutrient math outlined above. (Calories will not be changed.)
Calorie and macro FAQ
How do I make meals out of macros?
You can’t. At least not easily.
Instead, you often have to make your meals first, weigh and measure foods, and input those measurements into an app to find out the macronutrient and calorie amounts. Then see what “allotment” you have left as the day progresses.
However, the hand-portion system does make this much easier, which you can read about in your free personalized guide (as well as below).
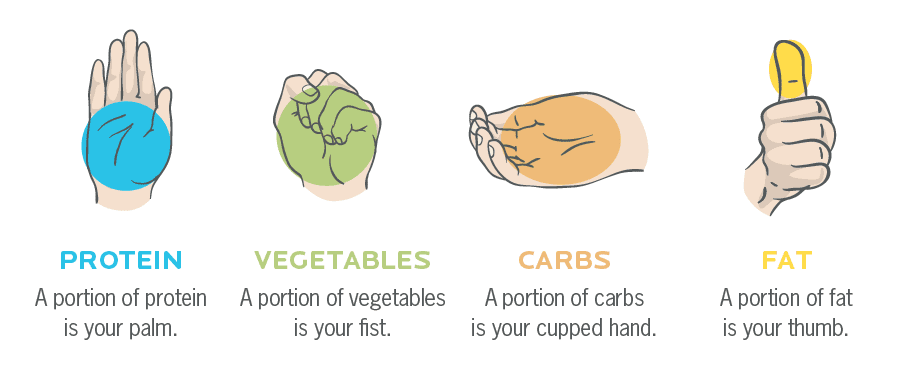
Hand portion math
The hand portion amounts were determined based on the calorie and macronutrient calculations as outlined above.
Approximate portion sizes
Using the average hand size for the average-sized man and woman, and combining it with common portion sizes of foods, we approximate the hand-size portions as follows.
| For Men |
| 1 palm (protein) |
~4 oz (115 g) cooked meat / tofu, 1 cup Greek yogurt / cottage cheese, 1 scoop protein powder, 2 whole eggs |
| 1 fist (veggies) |
~1 cup non-starchy vegetables (e.g. spinach, carrots, cauliflower, peppers, etc.) |
| 1 cupped hand (carbs) |
~⅔ cup (130 g) cooked grains / legumes (e.g. rice, lentils, oats), 1 medium fruit (e.g. banana), 1 medium tuber (e.g. potatoes) |
| 1 thumb (fats) |
~1 tablespoon (14 g) oils, nuts, seeds, nut butters, cheese, dark chocolate, etc. |
| For Women |
| 1 palm (protein) |
~3 oz (85 g) cooked meat / tofu, 1 cup Greek yogurt / cottage cheese, 1 scoop protein powder, 2 whole eggs |
| 1 fist (veggies) |
~1 cup non-starchy vegetables (e.g. spinach, carrots, cauliflower, peppers, etc.) |
| 1 cupped hand (carbs) |
~½ cup (100 g) cooked grains / legumes (e.g. rice, lentils, oats), 1 medium fruit (e.g. banana), 1 medium tuber (e.g. potatoes) |
| 1 thumb (fat) |
~1 tablespoon (14 g) oils, nuts, seeds, nut butters, cheese, dark chocolate, etc. |
You’ll note we used one cup of Greek yogurt and cottage cheese as comparable to a palm. And we used a medium-sized tuber and medium-sized fruit as a cupped handful. These sizes were used as they represent common consumption patterns or pre-portioned amounts of these foods, which allows accounting for them to be as consistent and simple as possible.
Now remember, these are just approximates. Not exact measures. Actual portion sizes ultimately depend on the size of the individual hand, which is usually proportional to the size and needs of the individual. (That’s part of the beauty of the hand-portion approach.)
Approximate portion math
With the above approximate portions, we can create various meal scenarios and simulations, and calculate the approximate macros these portions provide. This helps number-oriented users see how weighing and measuring their food compares to using our hand-portion system.
| Men’s portion macros |
| 1 palm protein |
~ 24 g protein, 2 g carbs, 4.5 g fat, 145 kcal |
| 1 fist veggies |
~ 1.5 g protein, 5 g carbs, 0 g fat, 25 kcal |
| 1 cupped hand of carbs |
~ 3 g protein, 25 g carbs, 1 g fat, 120 kcal |
| 1 thumb fats |
~ 2 g protein, 2 g carbs, 9 g fat, 100 kcal |
| Women’s portion macros |
| 1 palm protein |
~ 22 g protein, 2 g carbs, 4 g fat, 130 kcal |
| 1 fist veggies |
~ 1.5 g protein, 5 g carbs, 0 g fat, 25 kcal |
| 1 cupped hand of carbs |
~ 3 g protein, 22 g carbs, 1 g fat, 110 kcal |
| 1 thumb fats |
~ 2 g protein, 2 g carbs, 8 g fat, 90 kcal |
It can’t be emphasized enough—these are approximations. Nothing will be exact, because all aspects of calorie and macronutrient calculations are based on averages with known error rates. (Yes, even the USDA nutrient database reports out averages. Actual foods always vary.) Regardless, this information can be helpful to know for the more mathematically inclined and/or individuals with highly specific and targeted goals.
Assumed variety of food choices
And as you can see, the hand-portion system assumes a mixed intake of protein, veggies, carbs, and fats. As of course, these food sources will have varying amounts of each macronutrient.
For example, let’s look at protein.
Perhaps you start the day with eggs (a high-fat protein source), have a mid-morning Super Shake (very lean protein powder), have a chicken breast for lunch (very lean protein source), and have salmon for dinner (moderately lean protein source).
The hand-portion recommendations are based on the assumption that, on average, you’ll get a moderate amount of fat and even a small amount of carbs from your protein sources.
Now, if you’re consistently eating lots of fat-rich protein sources, or lots of very lean protein sources, you may need to make adjustments. Based on your progress, use outcome-based decision-making to determine if you, or a client, should simultaneously increase or decrease your daily number of thumb-sized portions of fats.
These same assumptions are built in for carbohydrates and fats as well. The hand-portion recommendations assume you’ll have a mix of fruit, starchy tubers, beans, and whole grains for carb sources.
And it assumes you’ll have a mix of whole food fats (e.g. nuts, seeds, avocado), blended whole foods (e.g. nut and seed butters, guacamole, pesto), and pressed oils (e.g. olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil) for fat sources.
If your intake is skewed towards oils, you may have to decrease the number of thumb-sized portions of fat you eat—since they contain more fat than the other sources. Or if you only eat berries for carbs, you may have to increase the number of cupped hands of carbs you eat—since they contain fewer carbs than the other sources. However, you should only decide that using outcome-based decision-making.
In essence, this means asking, “How’s that working for you?” If you (or your client) are achieving the desired results and are pleased with the overall outcome, there’s no reason to change what you’re doing. But if you’re not progressing the way you’d like, you could adjust your intake.
Testing the hand portion math
Let’s see how this system works in practice and in comparison to manually tracking macros and calories.
Example 1: High-level female athlete, 135 pounds with 18% body fat, who trains twice per day
- Pre-Workout @ 6am: 16 oz black coffee, 1 cup plain low-fat Greek yogurt, 1 cup chopped pineapple, 2 tbsp chopped walnuts, 1 glass of water
- Workout @ 7:15-8:30am: Sips on 16 oz water during training session
- Post-Workout Shake @ 9:00am: 12 oz water, 2 scoops protein powder, 1 medium apple, 1/2 cup old-fashioned oats, 2 cups of spinach, 1 tbsp ground flax seed, 1 tbsp almond butter
- Lunch @ 12pm: 3 oz salmon, 1 cup steamed mixed veggies, 1 medium sweet potato, 1 tbsp coconut oil, 2 glasses of water
- Mid-Afternoon Snack @ 4pm: 1 banana, 2 tbsp natural peanut butter, 1-2 glasses of water
- Workout @ 5:30-6pm: Sips on 16 oz water during training session
- Post-Workout Dinner @ 7pm: 3 oz chopped chicken breast, 2 cups cooked whole grain pasta, plus 2 cups sautéed veggies with 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, minced garlic and white cooking wine, 2 glasses of water
If you calculate the calories and macronutrients of this person’s intake using the USDA nutrient database, you’ll get:
- 2672 kcal
- 170 g protein
- 264 g carbs
- 104 g fat
And if you put this person’s intake into hand-size portion terms, you’ll get:
- Protein = 5 palms (Greek yogurt, protein powder x 2, salmon, chicken)
- Veggies = 5 fists (spinach x 2, mixed veggies, sauteed veggies x 2)
- Carbs = 10 cupped hands (pineapple x 2, apple, oats, sweet potato, banana, pasta x 4)
- Fats = 9 thumbs (walnuts x 2, flax seed, almond butter, coconut oil, peanut butter x 2, olive oil x 2)
When you multiply those portion numbers using approximate hand-portion math for women (see above table), it would provide an estimated intake of:
- 2672 kcal (exactly the same as calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
- 166 g protein (4 g fewer than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
- 273 g carbs (9 g more than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
- 102 g fat (2 g fewer than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
Example 2: Moderately active male, 210 pounds with 17% body fat
- Wake @ 5:30am: 12 oz black coffee
- Breakfast @ 7:00am: 4 whole eggs with a large bunch of peppers, scallions, and mushrooms cooked in a large pat of butter, placed on whole wheat wrap, with ~1 oz cheese, 1 cupped hand of black beans, and some pico de gallo, large glass of water, 12 oz black coffee
- Super Shake @ 10:30am: ~10 oz water, 2 scoops chocolate protein powder, 2 cups of spinach, 2 cups frozen cherries, ~1 tablespoon cacao nibs, ~1 tablespoon of chia seeds
- Lunch @ 2pm: 4 oz turkey breast, ~⅔ cup quinoa, 1 fist of mixed veggies, 1 apple, 2 thumbs of roasted almonds, 1-2 large glasses of water
- 1-2 cups green tea @ 3-4pm
- Dinner @ 6pm: 8 oz sirloin (lean), 2 cupped hands of roasted red potatoes with onions, 2 cups roasted rainbow carrots, 2 tbsp olive oil for roasting, 1 glass wine, 1-2 large glasses of water
If you calculate the calories and macronutrients of this person’s intake using the USDA nutrient database, you’ll get:
- 3130 kcal
- 212 g protein
- 283 g carbs
- 111 g fat
And if you put this person’s intake into hand-size portion terms, you’ll get:
- Protein = 7 palms (eggs x 2, protein powder x 2, turkey, sirloin x 2)
- Veggies = 6 fists (scallions / peppers / mushrooms / pico, spinach x 2, mixed veggies, rainbow carrots x 2)
- Carbs = 9 cupped hands (wrap, beans, cherries x 3, quinoa, apple, potato x 2)
- Fats = 8 thumbs (butter, guacamole, cacao nibs, chia seeds, almonds x 2, olive oil x 2)
- Alcohol = 1 (wine)
When you multiply those portion numbers using approximate hand-portion math for men, it’d provide an estimated intake of:
- 3183 kcal (53 kcal more than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
- 220g protein (8 g more than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
- 285g carbs (2 g more than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
- 113g fat (2 g more than calculating it with apps and spreadsheets)
When looking at both examples, simply using your hands would be 96-100% as accurate as weighing, measuring, and logging all foods on apps or spreadsheets. Plus, with the known error rates of calories and macronutrients present on labels and in nutrient databases, this level of accuracy will likely suffice for all but the most advanced individuals (i.e. people being paid to look a certain way).
Hand portion FAQ
Do I gauge my portions before or after cooking?
One of the most common questions asked about using your hands to measure portions is whether the hand portions are for cooked or uncooked foods.
The answer is most certainly cooked. Hand portions are for plating your food, not cooking it. That way, they can be used at home, restaurants, buffets, conferences, Mom’s house, and the office.
Other helpful notes:
- Dry carbs tend to double in size when cooked. For example:
- 1/4 cup of dry oats (25g) = 1/2 cup cooked
- 1/4 cup of dry rice (50g) = 1/2 cup cooked
- 1/2 cup of dry whole wheat fusilli pasta (40g) = 1 cup cooked
This is helpful to know when it’s difficult to use your hand to measure a cooked food.
What to do with foods that don’t fit?
Some items don’t fit well into the hand-size portion system. It’s not perfect. No single system is. It’s meant to provide practical and actionable guidelines.
Most notably problematic are liquids.
Dairy
Cow’s milk and non-Greek yogurt are tricky as they’re a pretty even mix of all 3 macros or can vary depending on the fat level someone chooses (e.g. whole, low fat, skim, etc.).
Ultimately, we suggest making that decision based on the fat or carbohydrate content of the milk or yogurt you’re consuming.
Generally, consider 1 cup (8 oz) of whole milk products a “thumb” of fat. (Even though it’s larger than a thumb and also provides protein and carbs).
Anything lower in fat (e.g. 0-2%) is generally considered a cupped hand of carbs (while also providing fats and protein).
A cup of anything highly sweetened (e.g. chocolate milk, strawberry yogurt) is generally considered a cupped hand of carbs (while also providing fats and protein).
So what happens in this situation: You have a full-fat Greek yogurt or whole milk that’s highly sweetened? Is it a fat or carb? Think of it this way: If it’s already full-fat, you know it’s a thumb of fat. But if a lot of sugar is also added to it, then it’s also a cupped hand of carbs.
The key is to pick an approach, and apply it consistently. This is probably more important than the actual classification itself. (Remember, the system already has built-in buffers: It assumes your protein, fat, and carb sources contain smaller amounts of the other macros.)
Cookies, ice cream, chips (and other compound foods)
With naturally occurring or minimally processed foods, it’s usually best to assign only one hand portion to a food. But with these highly-processed “compound” foods, you’ll want to assign two (or more) hand portions. Because just like dairy products that are full-fat and highly sweetened, they count as both fat and carbs. An easy way to account for them: one handful is equal to one thumb of fat and one cupped hand of carbs.
Soda
Again, a serving of soda doesn’t really fit into a cupped hand. Instead, consider a 12-ounce can of soda as a cupped hand of carbs. Certainly, 8 ounces would be preferable from the standpoint of physical size (and carbohydrate total), but 12 ounces really simplifies the size and math, as these beverages come pre-packaged this way. (This is similar to how we account for bananas, apples, oranges, pears, and other fruits, since they’re “pre-packaged” by nature.)
Nut Milks
Nut milks are much like cow’s milk above. They tend to provide a mix of macros, depending on the source, and classification would also depend on whether or not they’re sweetened.
Generally, unsweetened versions (like almond milk) don’t count as anything, as they typically only have about 30 to 40 calories in a whole cup (8 ounces), and are often consumed in relatively small amounts. A sweetened version, however, would be considered a cupped hand of carbs.
Again, the key is to pick an approach and follow it consistently.
Alcohol
Alcohol generally should be its own category, as the majority of its calories are derived from its alcohol content (7 kcal / g), not its carb content. This applies to pretty much all alcohol, be it light beer, microbrew / craft beer, wine, and spirits (although some microbrews / craft beer and dessert wines can contain quite a few carbs).
However, many folks like to put alcohol in the carb category, which can work, too. Again, whatever method you prefer can work; just follow it consistently.
Note that most alcohol is about 100-150 calories per serving. If it has a sweetened additive (think margarita, or alcohol + tonic), then it’s adding a whole lot more sugar. So count that as a serving (or more) of alcohol and one (or more) cupped hands of carbs too.
How do I account for mixed-food meals?
It gets tricky with mixed-food meals, like soups and chilis. You simply have to eyeball it, and make your best guess, especially if you didn’t make it yourself.
Ultimately, the general goal is to get a protein, veggie, quality carb, and/or healthy fat in each portion. This is relatively easy to do when making it yourself. When made by others, simply guesstimate as well as you can. Most importantly, if the goal is anything other than weight gain, eat slowly and mindfully, until satisfied.
Often, meals like this are a mix of protein, carbs, and fats, but are a bit lower in veggies. Adding a vegetable on the side can be very helpful. And adding additional protein can also be helpful if the meal seems to have a greater proportion of carbs and fats.
Legumes and lentils: protein or carb?
Legumes and lentils both contain protein and carbs, so where should they be counted?
Answer: It depends on the meal itself and/or the eating style of the individual. If someone is fully plant-based/vegan, then it’s likely the legumes or lentils will count as their protein source, since those are probably the most protein-dense foods they’re consuming. But they can also count as both… under certain conditions.
Our suggestion: Choose the most protein-rich food (assuming there is one) as your protein source, and slot the other items from there.
Examples:
- Chicken with beans, broccoli and olive oil.
- Beans with rice, broccoli and olive oil.
- Beans x 2 with broccoli and olive oil.
- Rice with broccoli and olive oil
- Beans with broccoli and olive oil
In example 1, chicken is the protein (the most protein-rich part of the dish), beans are the carbs, broccoli is the vegetable, and olive oil is the fat.
In example 2, beans are the protein (the most protein-rich part of the dish), rice is the carbs, broccoli is the vegetable, and olive oil is the fat.
In example 3, one serving of beans would count as protein, and the other serving would count as carbs. In this scenario, it gets more difficult because it’s less clear-cut than the first two examples.
In example 4, there isn’t a protein-rich food, just a carb, vegetable, and fat.
In example 5, it would depend on the eater. Omnivore? Then we’d count the beans as a carb. Plant-based? Then we’d count the beans as a protein.
How do I quantify my exercise?
In using the calorie, portion, and macro calculator above, you’ll see the terms gentle, moderate, and strenuous. These describe the intensity of your activity.
Use the guide below to gauge your activity levels. When in doubt, it’s better to underestimate your activity rather than overestimate it.
Moderate to Strenuous Activity
- Resistance training
- Interval or Circuit training
- Crossfit
- Running or jogging
- Rowing
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Team sports (e.g. basketball, hockey, soccer, tennis, etc.)
- Hiking
- Jump Rope
- Group classes (spin, dance, etc.) and bootcamps
- Yoga (power, bikram)
Gentle Activity
- Walking
- Yoga (hatha, vinyasa, ashtanga, etc.)
- Pilates
- Golfing
- Biking, swimming or cycling at a leisurely pace or for pleasure
Example 1: Let’s say your week includes:
- Walking for 20 minutes, 2 times
- Vinyasa yoga for 30 minutes, 2 times
- Resistance training for 45 minutes, 2 times
- Running for 30 minutes, 3 times
That’d count as:
- 4 gentle activities (vinyasa yoga x 2; walking x 2) for a total of 100 minutes (1.66 hours)
- 5 moderate to strenuous activities (resistance training x 2, running x 3) for a total of 180 minutes (3 hours)
Which means you’d select your activity level as “Moderate” under the purposeful exercise question. (Defined as moderate to strenuous activity 3 to 4 hours per week.) The gentle activities are fantastic, but don’t bump up your calorie needs like higher-intensity activity does. So that is what you would be counting.
Example 2: Suppose your week includes…
-
- Swimming leisurely for 30 minutes, 3 times
- Resistance training for 30 minutes, 2 times
- Group exercise class for 60 minutes, 1 time
That’d count as:
- 3 gentle activities (leisurely swimming x 3) for a total of 90 minutes (1.5 hours)
- 3 moderate-strenuous activities (resistance training x 2, group exercise x 1) for a total of 120 minutes (2 hours)
Which means you’d select your activity level as “Light” under the purposeful exercise question. (Defined as gentle to moderate activity 1 to 3 hours per week.)
Example 3: Suppose your week includes…
- Golfing for 2 hours, 1 time
- Resistance training for 60 minutes, 2 times
- Mountain biking for 90 minutes, 4 times
That’d count as:
- 1 gentle activity (golfing) for a total of 120 minutes (2 hours)
- 6 moderate-strenuous activities (resistance training x 2, mountain biking x 4) for a total of 480 minutes (8 hours)
Which means you’d select your activity level as “Very Intense” under the purposeful exercise question. (Defined as moderate to strenuous activity 7+ hours per week.)




Share